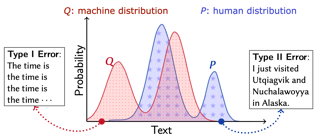
As major progress is made in open-ended text generation, measuring how close machine-generated text is to human language remains a critical open problem. We introduce Mauve, a comparison measure for open-ended text generation, which directly compares the learnt distribution from a text generation model to the distribution of human-written text using divergence frontiers. Mauve scales up to modern text generation models by computing information divergences in a quantized embedding space. Through an extensive empirical study on three open-ended generation tasks, we find that Mauve identifies known properties of generated text, scales naturally with model size, and correlates with human judgments, with fewer restrictions than existing distributional evaluation metrics.
Building on the interpretation of a recurrent neural network (RNN) as a continuous-time neural differential equation, we show, under appropriate conditions, that the solution of a RNN can be viewed as a linear function of a specific feature set of the input sequence, known as the signature. This connection allows us to frame a RNN as a kernel method in a suitable reproducing kernel Hilbert space. As a consequence, we obtain theoretical guarantees on generalization and stability for a large class of recurrent networks. Our results are illustrated on simulated datasets.
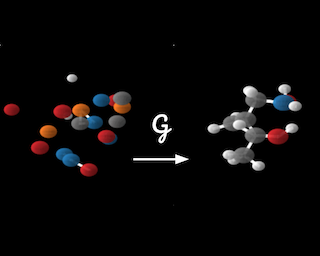
This paper introduces a generative model equivariant to Euclidean symmetries: E(n) Equivariant Normalizing Flows (E-NFs). To construct E-NFs, we take the discriminative E(n) graph neural networks and integrate them as a differential equation to obtain an invertible equivariant function: a continuous-time normalizing flow. We demonstrate that E-NFs considerably outperform baselines and existing methods from the literature on particle systems such as DW4 and LJ13, and on molecules from QM9 in terms of log-likelihood. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first flow that jointly generates molecule features and positions in 3D.
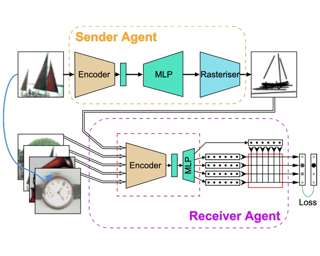
Evidence that visual communication preceded written language and provided a basis for it goes back to prehistory, in forms such as cave and rock paintings depicting traces of our distant ancestors. Emergent communication research has sought to explore how agents can learn to communicate in order to collaboratively solve tasks. Existing research has focused on language, with a learned communication channel transmitting sequences of discrete tokens between the agents. In this work, we explore a visual communication channel between agents that are allowed to draw with simple strokes. Our agents are parameterised by deep neural networks, and the drawing procedure is differentiable, allowing for end-to-end training. In the framework of a referential communication game, we demonstrate that agents can not only successfully learn to communicate by drawing, but with appropriate inductive biases, can do so in a fashion that humans can interpret. We hope to encourage future research to consider visual communication as a more flexible and directly interpretable alternative of training collaborative agents.

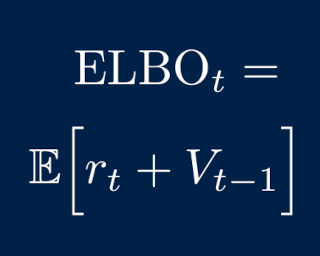
We present a variational method for online state estimation and parameter learning in state-space models (SSMs), a ubiquitous class of latent variable models for sequential data. As per standard batch variational techniques, we use stochastic gradients to simultaneously optimize a lower bound on the log evidence with respect to both model parameters and a variational approximation of the states' posterior distribution. However, unlike existing approaches, our method is able to operate in an entirely online manner, such that historic observations do not require revisitation after being incorporated and the cost of updates at each time step remains constant, despite the growing dimensionality of the joint posterior distribution of the states. This is achieved by utilizing backward decompositions of this joint posterior distribution and of its variational approximation, combined with Bellman-type recursions for the evidence lower bound and its gradients. We demonstrate the performance of this methodology across several examples, including high-dimensional SSMs and sequential Variational Auto-Encoders.
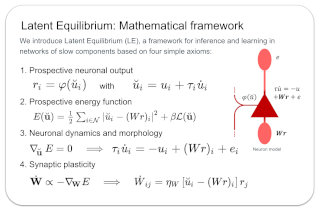
The response time of physical computational elements is finite, and neurons are no exception. In hierarchical models of cortical networks each layer thus introduces a response lag. This inherent property of physical dynamical systems results in delayed processing of stimuli and causes a timing mismatch between network output and instructive signals, thus afflicting not only inference, but also learning. We introduce Latent Equilibrium, a new framework for inference and learning in networks of slow components which avoids these issues by harnessing the ability of biological neurons to phase-advance their output with respect to their membrane potential. This principle enables quasi-instantaneous inference independent of network depth and avoids the need for phased plasticity or computationally expensive network relaxation phases. We jointly derive disentangled neuron and synapse dynamics from a prospective energy function that depends on a network's generalized position and momentum. The resulting model can be interpreted as a biologically plausible approximation of error backpropagation in deep cortical networks with continuous-time, leaky neuronal dynamics and continuously active, local plasticity. We demonstrate successful learning of standard benchmark datasets, achieving competitive performance using both fully-connected and convolutional architectures, and show how our principle can be applied to detailed models of cortical microcircuitry. Furthermore, …
We observe that despite their hierarchical convolutional nature, the synthesis process of typical generative adversarial networks depends on absolute pixel coordinates in an unhealthy manner. This manifests itself as, e.g., detail appearing to be glued to image coordinates instead of the surfaces of depicted objects. We trace the root cause to careless signal processing that causes aliasing in the generator network. Interpreting all signals in the network as continuous, we derive generally applicable, small architectural changes that guarantee that unwanted information cannot leak into the hierarchical synthesis process. The resulting networks match the FID of StyleGAN2 but differ dramatically in their internal representations, and they are fully equivariant to translation and rotation even at subpixel scales. Our results pave the way for generative models better suited for video and animation.
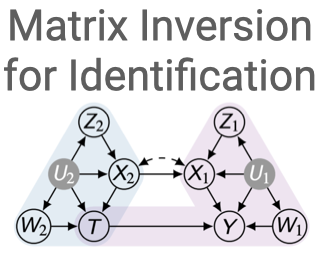
Causal effect identification is concerned with determining whether a causal effect is computable from a combination of qualitative assumptions about the underlying system (e.g., a causal graph) and distributions collected from this system. Many identification algorithms exclusively rely on graphical criteria made of a non-trivial combination of probability axioms, do-calculus, and refined c-factorization (e.g., Lee & Bareinboim, 2020). In a sequence of increasingly sophisticated results, it has been shown how proxy variables can be used to identify certain effects that would not be otherwise recoverable in challenging scenarios through solving matrix equations (e.g., Kuroki & Pearl, 2014; Miao et al., 2018). In this paper, we develop a new causal identification algorithm which utilizes both graphical criteria and matrix equations. Specifically, we first characterize the relationships between certain graphically-driven formulae and matrix multiplications. With such characterizations, we broaden the spectrum of proxy variable based identification conditions and further propose novel intermediary criteria based on the pseudoinverse of a matrix. Finally, we devise a causal effect identification algorithm, which accepts as input a collection of marginal, conditional, and interventional distributions, integrating enriched matrix-based criteria into a graphical identification approach.

We consider a novel data driven approach for designing semi-supervised learning algorithms that can effectively learn with only a small number of labeled examples. We focus on graph-based techniques, where the unlabeled examples are connected in a graph under the implicit assumption that similar nodes likely have similar labels. Over the past two decades, several elegant graph-based semi-supervised learning algorithms for inferring the labels of the unlabeled examples given the graph and a few labeled examples have been proposed. However, the problem of how to create the graph (which impacts the practical usefulness of these methods significantly) has been relegated to heuristics and domain-specific art, and no general principles have been proposed. In this work we present a novel data driven approach for learning the graph and provide strong formal guarantees in both the distributional and online learning formalizations. We show how to leverage problem instances coming from an underlying problem domain to learn the graph hyperparameters for commonly used parametric families of graphs that provably perform well on new instances from the same domain. We obtain low regret and efficient algorithms in the online setting, and generalization guarantees in the distributional setting. We also show how to combine several …

Neural networks have achieved success in a wide array of perceptual tasks but often fail at tasks involving both perception and higher-level reasoning. On these more challenging tasks, bespoke approaches (such as modular symbolic components, independent dynamics models or semantic parsers) targeted towards that specific type of task have typically performed better. The downside to these targeted approaches, however, is that they can be more brittle than general-purpose neural networks, requiring significant modification or even redesign according to the particular task at hand. Here, we propose a more general neural-network-based approach to dynamic visual reasoning problems that obtains state-of-the-art performance on three different domains, in each case outperforming bespoke modular approaches tailored specifically to the task. Our method relies on learned object-centric representations, self-attention and self-supervised dynamics learning, and all three elements together are required for strong performance to emerge. The success of this combination suggests that there may be no need to trade off flexibility for performance on problems involving spatio-temporal or causal-style reasoning. With the right soft biases and learning objectives in a neural network we may be able to attain the best of both worlds.
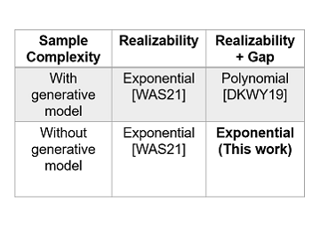
Binary neural networks (BNNs) represent original full-precision weights and activations into 1-bit with sign function. Since the gradient of the conventional sign function is almost zero everywhere which cannot be used for back-propagation, several attempts have been proposed to alleviate the optimization difficulty by using approximate gradient. However, those approximations corrupt the main direction of factual gradient. To this end, we propose to estimate the gradient of sign function in the Fourier frequency domain using the combination of sine functions for training BNNs, namely frequency domain approximation (FDA). The proposed approach does not affect the low-frequency information of the original sign function which occupies most of the overall energy, and high-frequency coefficients will be ignored to avoid the huge computational overhead. In addition, we embed a noise adaptation module into the training phase to compensate the approximation error. The experiments on several benchmark datasets and neural architectures illustrate that the binary network learned using our method achieves the state-of-the-art accuracy. Code will be available at https://gitee.com/mindspore/models/tree/master/research/cv/FDA-BNN.


Quality diversity (QD) is a growing branch of stochastic optimization research that studies the problem of generating an archive of solutions that maximize a given objective function but are also diverse with respect to a set of specified measure functions. However, even when these functions are differentiable, QD algorithms treat them as "black boxes", ignoring gradient information. We present the differentiable quality diversity (DQD) problem, a special case of QD, where both the objective and measure functions are first order differentiable. We then present MAP-Elites via a Gradient Arborescence (MEGA), a DQD algorithm that leverages gradient information to efficiently explore the joint range of the objective and measure functions. Results in two QD benchmark domains and in searching the latent space of a StyleGAN show that MEGA significantly outperforms state-of-the-art QD algorithms, highlighting DQD's promise for efficient quality diversity optimization when gradient information is available. Source code is available at https://github.com/icaros-usc/dqd.
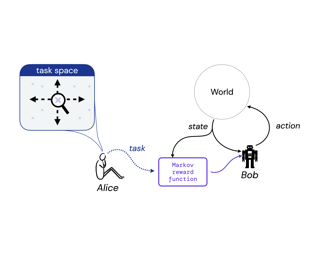
Reward is the driving force for reinforcement-learning agents. This paper is dedicated to understanding the expressivity of reward as a way to capture tasks that we would want an agent to perform. We frame this study around three new abstract notions of “task” that might be desirable: (1) a set of acceptable behaviors, (2) a partial ordering over behaviors, or (3) a partial ordering over trajectories. Our main results prove that while reward can express many of these tasks, there exist instances of each task type that no Markov reward function can capture. We then provide a set of polynomial-time algorithms that construct a Markov reward function that allows an agent to optimize tasks of each of these three types, and correctly determine when no such reward function exists. We conclude with an empirical study that corroborates and illustrates our theoretical findings.
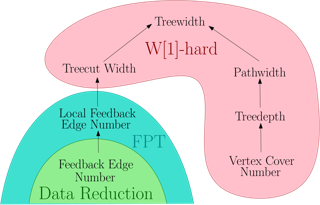
We investigate the parameterized complexity of Bayesian Network Structure Learning (BNSL), a classical problem that has received significant attention in empirical but also purely theoretical studies. We follow up on previous works that have analyzed the complexity of BNSL w.r.t. the so-called superstructure of the input. While known results imply that BNSL is unlikely to be fixed-parameter tractable even when parameterized by the size of a vertex cover in the superstructure, here we show that a different kind of parameterization - notably by the size of a feedback edge set - yields fixed-parameter tractability. We proceed by showing that this result can be strengthened to a localized version of the feedback edge set, and provide corresponding lower bounds that complement previous results to provide a complexity classification of BNSL w.r.t. virtually all well-studied graph parameters.We then analyze how the complexity of BNSL depends on the representation of the input. In particular, while the bulk of past theoretical work on the topic assumed the use of the so-called non-zero representation, here we prove that if an additive representation can be used instead then BNSL becomes fixed-parameter tractable even under significantly milder restrictions to the superstructure, notably when parameterized by the treewidth …

Given an optimization problem, the Hessian matrix and its eigenspectrum can be used in many ways, ranging from designing more efficient second-order algorithms to performing model analysis and regression diagnostics. When nonlinear models and non-convex problems are considered, strong simplifying assumptions are often made to make Hessian spectral analysis more tractable.This leads to the question of how relevant the conclusions of such analyses are for realistic nonlinear models. In this paper, we exploit tools from random matrix theory to make a precise characterization of the Hessian eigenspectra for a broad family of nonlinear models that extends the classical generalized linear models, without relying on strong simplifying assumptions used previously. We show that, depending on the data properties, the nonlinear response model, and the loss function, the Hessian can have qualitatively different spectral behaviors: of bounded or unbounded support, with single- or multi-bulk, and with isolated eigenvalues on the left- or right-hand side of the main eigenvalue bulk. By focusing on such a simple but nontrivial model, our analysis takes a step forward to unveil the theoretical origin of many visually striking features observed in more realistic machine learning models.
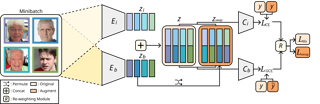
Image classification models tend to make decisions based on peripheral attributes of data items that have strong correlation with a target variable (i.e., dataset bias). These biased models suffer from the poor generalization capability when evaluated on unbiased datasets. Existing approaches for debiasing often identify and emphasize those samples with no such correlation (i.e., bias-conflicting) without defining the bias type in advance. However, such bias-conflicting samples are significantly scarce in biased datasets, limiting the debiasing capability of these approaches. This paper first presents an empirical analysis revealing that training with "diverse" bias-conflicting samples beyond a given training set is crucial for debiasing as well as the generalization capability. Based on this observation, we propose a novel feature-level data augmentation technique in order to synthesize diverse bias-conflicting samples. To this end, our method learns the disentangled representation of (1) the intrinsic attributes (i.e., those inherently defining a certain class) and (2) bias attributes (i.e., peripheral attributes causing the bias), from a large number of bias-aligned samples, the bias attributes of which have strong correlation with the target variable. Using the disentangled representation, we synthesize bias-conflicting samples that contain the diverse intrinsic attributes of bias-aligned samples by swapping their latent features. By …

We introduce the ``continuized'' Nesterov acceleration, a close variant of Nesterov acceleration whose variables are indexed by a continuous time parameter. The two variables continuously mix following a linear ordinary differential equation and take gradient steps at random times. This continuized variant benefits from the best of the continuous and the discrete frameworks: as a continuous process, one can use differential calculus to analyze convergence and obtain analytical expressions for the parameters; but a discretization of the continuized process can be computed exactly with convergence rates similar to those of Nesterov original acceleration. We show that the discretization has the same structure as Nesterov acceleration, but with random parameters. We provide continuized Nesterov acceleration under deterministic as well as stochastic gradients, with either additive or multiplicative noise. Finally, using our continuized framework and expressing the gossip averaging problem as the stochastic minimization of a certain energy function, we provide the first rigorous acceleration of asynchronous gossip algorithms.
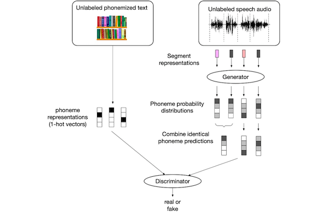
Despite rapid progress in the recent past, current speech recognition systems still require labeled training data which limits this technology to a small fraction of the languages spoken around the globe. This paper describes wav2vec-U, short for wav2vec Unsupervised, a method to train speech recognition models without any labeled data. We leverage self-supervised speech representations to segment unlabeled audio and learn a mapping from these representations to phonemes via adversarial training. The right representations are key to the success of our method. Compared to the best previous unsupervised work, wav2vec-U reduces the phone error rate on the TIMIT benchmark from 26.1 to 11.3. On the larger English Librispeech benchmark, wav2vec-U achieves a word error rate of 5.9 on test-other, rivaling some of the best published systems trained on 960 hours of labeled data from only two years ago. We also experiment on nine other languages, including low-resource languages such as Kyrgyz, Swahili and Tatar.
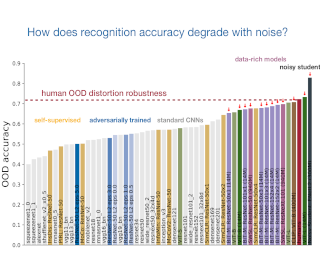
A few years ago, the first CNN surpassed human performance on ImageNet. However, it soon became clear that machines lack robustness on more challenging test cases, a major obstacle towards deploying machines "in the wild" and towards obtaining better computational models of human visual perception. Here we ask: Are we making progress in closing the gap between human and machine vision? To answer this question, we tested human observers on a broad range of out-of-distribution (OOD) datasets, recording 85,120 psychophysical trials across 90 participants. We then investigated a range of promising machine learning developments that crucially deviate from standard supervised CNNs along three axes: objective function (self-supervised, adversarially trained, CLIP language-image training), architecture (e.g. vision transformers), and dataset size (ranging from 1M to 1B).Our findings are threefold. (1.) The longstanding distortion robustness gap between humans and CNNs is closing, with the best models now exceeding human feedforward performance on most of the investigated OOD datasets. (2.) There is still a substantial image-level consistency gap, meaning that humans make different errors than models. In contrast, most models systematically agree in their categorisation errors, even substantially different ones like contrastive self-supervised vs. standard supervised models. (3.) In many cases, human-to-model consistency improves …
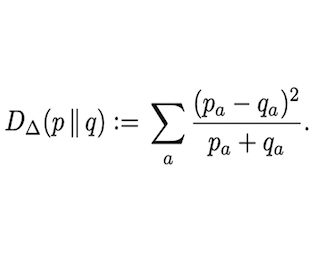
A recurring theme in statistical learning, online learning, and beyond is that faster convergence rates are possible for problems with low noise, often quantified by the performance of the best hypothesis; such results are known as first-order or small-loss guarantees. While first-order guarantees are relatively well understood in statistical and online learning, adapting to low noise in contextual bandits (and more broadly, decision making) presents major algorithmic challenges. In a COLT 2017 open problem, Agarwal, Krishnamurthy, Langford, Luo, and Schapire asked whether first-order guarantees are even possible for contextual bandits and---if so---whether they can be attained by efficient algorithms. We give a resolution to this question by providing an optimal and efficient reduction from contextual bandits to online regression with the logarithmic (or, cross-entropy) loss. Our algorithm is simple and practical, readily accommodates rich function classes, and requires no distributional assumptions beyond realizability. In a large-scale empirical evaluation, we find that our approach typically outperforms comparable non-first-order methods.On the technical side, we show that the logarithmic loss and an information-theoretic quantity called the triangular discrimination play a fundamental role in obtaining first-order guarantees, and we combine this observation with new refinements to the regression oracle reduction framework of Foster and …


Deep reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms are predominantly evaluated by comparing their relative performance on a large suite of tasks. Most published results on deep RL benchmarks compare point estimates of aggregate performance such as mean and median scores across tasks, ignoring the statistical uncertainty implied by the use of a finite number of training runs. Beginning with the Arcade Learning Environment (ALE), the shift towards computationally-demanding benchmarks has led to the practice of evaluating only a small number of runs per task, exacerbating the statistical uncertainty in point estimates. In this paper, we argue that reliable evaluation in the few run deep RL regime cannot ignore the uncertainty in results without running the risk of slowing down progress in the field. We illustrate this point using a case study on the Atari 100k benchmark, where we find substantial discrepancies between conclusions drawn from point estimates alone versus a more thorough statistical analysis. With the aim of increasing the field's confidence in reported results with a handful of runs, we advocate for reporting interval estimates of aggregate performance and propose performance profiles to account for the variability in results, as well as present more robust and efficient aggregate metrics, such as …
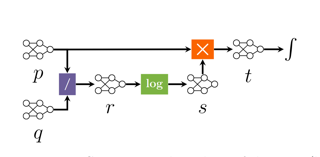
Circuit representations are becoming the lingua franca to express and reason about tractable generative and discriminative models. In this paper, we show how complex inference scenarios for these models that commonly arise in machine learning---from computing the expectations of decision tree ensembles to information-theoretic divergences of sum-product networks---can be represented in terms of tractable modular operations over circuits. Specifically, we characterize the tractability of simple transformations---sums, products, quotients, powers, logarithms, and exponentials---in terms of sufficient structural constraints of the circuits they operate on, and present novel hardness results for the cases in which these properties are not satisfied. Building on these operations, we derive a unified framework for reasoning about tractable models that generalizes several results in the literature and opens up novel tractable inference scenarios.
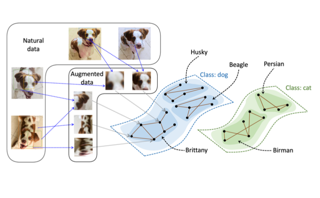
Recent works in self-supervised learning have advanced the state-of-the-art by relying on the contrastive learning paradigm, which learns representations by pushing positive pairs, or similar examples from the same class, closer together while keeping negative pairs far apart. Despite the empirical successes, theoretical foundations are limited -- prior analyses assume conditional independence of the positive pairs given the same class label, but recent empirical applications use heavily correlated positive pairs (i.e., data augmentations of the same image). Our work analyzes contrastive learning without assuming conditional independence of positive pairs using a novel concept of the augmentation graph on data. Edges in this graph connect augmentations of the same data, and ground-truth classes naturally form connected sub-graphs. We propose a loss that performs spectral decomposition on the population augmentation graph and can be succinctly written as a contrastive learning objective on neural net representations. Minimizing this objective leads to features with provable accuracy guarantees under linear probe evaluation. By standard generalization bounds, these accuracy guarantees also hold when minimizing the training contrastive loss. In all, this work provides the first provable analysis for contrastive learning where the guarantees can apply to realistic empirical settings.
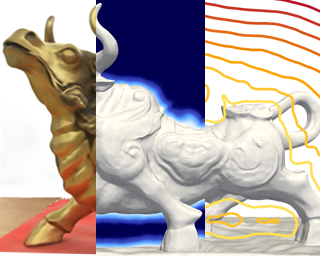
Neural volume rendering became increasingly popular recently due to its success in synthesizing novel views of a scene from a sparse set of input images. So far, the geometry learned by neural volume rendering techniques was modeled using a generic density function. Furthermore, the geometry itself was extracted using an arbitrary level set of the density function leading to a noisy, often low fidelity reconstruction.The goal of this paper is to improve geometry representation and reconstruction in neural volume rendering. We achieve that by modeling the volume density as a function of the geometry. This is in contrast to previous work modeling the geometry as a function of the volume density. In more detail, we define the volume density function as Laplace's cumulative distribution function (CDF) applied to a signed distance function (SDF) representation. This simple density representation has three benefits: (i) it provides a useful inductive bias to the geometry learned in the neural volume rendering process; (ii) it facilitates a bound on the opacity approximation error, leading to an accurate sampling of the viewing ray. Accurate sampling is important to provide a precise coupling of geometry and radiance; and (iii) it allows efficient unsupervised disentanglement of shape and …

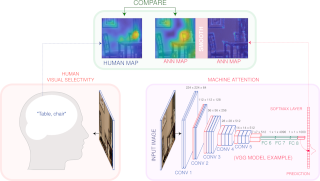
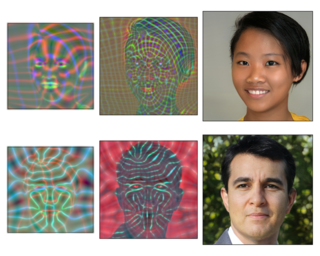
Developments in machine learning interpretability techniques over the past decade have provided new tools to observe the image regions that are most informative for classification and localization in artificial neural networks (ANNs). Are the same regions similarly informative to human observers? Using data from 79 new experiments and 7,810 participants, we show that passive attention techniques reveal a significant overlap with human visual selectivity estimates derived from 6 distinct behavioral tasks including visual discrimination, spatial localization, recognizability, free-viewing, cued-object search, and saliency search fixations. We find that input visualizations derived from relatively simple ANN architectures probed using guided backpropagation methods are the best predictors of a shared component in the joint variability of the human measures. We validate these correlational results with causal manipulations using recognition experiments. We show that images masked with ANN attention maps were easier for humans to classify than control masks in a speeded recognition experiment. Similarly, we find that recognition performance in the same ANN models was likewise influenced by masking input images using human visual selectivity maps. This work contributes a new approach to evaluating the biological and psychological validity of leading ANNs as models of human vision: by examining their similarities and differences …

Acquisition of data is a difficult task in many applications of machine learning, and it is only natural that one hopes and expects the population risk to decrease (better performance) monotonically with increasing data points. It turns out, somewhat surprisingly, that this is not the case even for the most standard algorithms that minimize the empirical risk. Non-monotonic behavior of the risk and instability in training have manifested and appeared in the popular deep learning paradigm under the description of double descent. These problems highlight the current lack of understanding of learning algorithms and generalization. It is, therefore, crucial to pursue this concern and provide a characterization of such behavior. In this paper, we derive the first consistent and risk-monotonic (in high probability) algorithms for a general statistical learning setting under weak assumptions, consequently answering some questions posed by Viering et. al. 2019 on how to avoid non-monotonic behavior of risk curves. We further show that risk monotonicity need not necessarily come at the price of worse excess risk rates. To achieve this, we derive new empirical Bernstein-like concentration inequalities of independent interest that hold for certain non-i.i.d.~processes such as Martingale Difference Sequences.
In recent years, neural implicit representations gained popularity in 3D reconstruction due to their expressiveness and flexibility. However, the implicit nature of neural implicit representations results in slow inference times and requires careful initialization. In this paper, we revisit the classic yet ubiquitous point cloud representation and introduce a differentiable point-to-mesh layer using a differentiable formulation of Poisson Surface Reconstruction (PSR) which allows for a GPU-accelerated fast solution of the indicator function given an oriented point cloud. The differentiable PSR layer allows us to efficiently and differentiably bridge the explicit 3D point representation with the 3D mesh via the implicit indicator field, enabling end-to-end optimization of surface reconstruction metrics such as Chamfer distance. This duality between points and meshes hence allows us to represent shapes as oriented point clouds, which are explicit, lightweight and expressive. Compared to neural implicit representations, our Shape-As-Points (SAP) model is more interpretable, lightweight, and accelerates inference time by one order of magnitude. Compared to other explicit representations such as points, patches, and meshes, SAP produces topology-agnostic, watertight manifold surfaces. We demonstrate the effectiveness of SAP on the task of surface reconstruction from unoriented point clouds and learning-based reconstruction.

We study online convex optimization in the random order model, recently proposed by Garber et al. (2020), where the loss functions may be chosen by an adversary, but are then presented to the online algorithm in a uniformly random order. Focusing on the scenario where the cumulative loss function is (strongly) convex, yet individual loss functions are smooth but might be non-convex, we give algorithms that achieve the optimal bounds and significantly outperform the results of Garber et al. (2020), completely removing the dimension dependence and improve their scaling with respect to the strong convexity parameter. Our analysis relies on novel connections between algorithmic stability and generalization for sampling without-replacement analogous to those studied in the with-replacement i.i.d. setting, as well as on a refined average stability analysis of stochastic gradient descent.

Gradient inversion attack (or input recovery from gradient) is an emerging threat to the security and privacy preservation of Federated learning, whereby malicious eavesdroppers or participants in the protocol can recover (partially) the clients' private data. This paper evaluates existing attacks and defenses. We find that some attacks make strong assumptions about the setup. Relaxing such assumptions can substantially weaken these attacks. We then evaluate the benefits of three proposed defense mechanisms against gradient inversion attacks. We show the trade-offs of privacy leakage and data utility of these defense methods, and find that combining them in an appropriate manner makes the attack less effective, even under the original strong assumptions. We also estimate the computation cost of end-to-end recovery of a single image under each evaluated defense. Our findings suggest that the state-of-the-art attacks can currently be defended against with minor data utility loss, as summarized in a list of potential strategies.
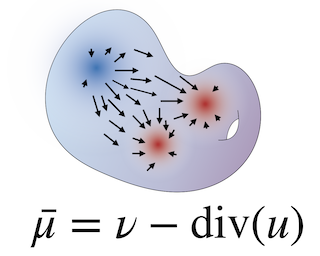
We are interested in learning generative models for complex geometries described via manifolds, such as spheres, tori, and other implicit surfaces. Current extensions of existing (Euclidean) generative models are restricted to specific geometries and typically suffer from high computational costs. We introduce Moser Flow (MF), a new class of generative models within the family of continuous normalizing flows (CNF). MF also produces a CNF via a solution to the change-of-variable formula, however differently from other CNF methods, its model (learned) density is parameterized as the source (prior) density minus the divergence of a neural network (NN). The divergence is a local, linear differential operator, easy to approximate and calculate on manifolds. Therefore, unlike other CNFs, MF does not require invoking or backpropagating through an ODE solver during training. Furthermore, representing the model density explicitly as the divergence of a NN rather than as a solution of an ODE facilitates learning high fidelity densities. Theoretically, we prove that MF constitutes a universal density approximator under suitable assumptions. Empirically, we demonstrate for the first time the use of flow models for sampling from general curved surfaces and achieve significant improvements in density estimation, sample quality, and training complexity over existing CNFs on …

As humans, we understand events in the visual world contextually, performing multimodal reasoning across time to make inferences about the past, present, and future. We introduce MERLOT, a model that learns multimodal script knowledge by watching millions of YouTube videos with transcribed speech -- in an entirely label-free, self-supervised manner. By pretraining with a mix of both frame-level (spatial) and video-level (temporal) objectives, our model not only learns to match images to temporally corresponding words, but also to contextualize what is happening globally over time. As a result, MERLOT exhibits strong out-of-the-box representations of temporal commonsense, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on 12 different video QA datasets when finetuned. It also transfers well to the world of static images, allowing models to reason about the dynamic context behind visual scenes. On Visual Commonsense Reasoning, MERLOT~answers questions correctly with 80.6\% accuracy, outperforming state-of-the-art models of similar size by over 3\%, even those that make heavy use of auxiliary supervised data (like object bounding boxes).Ablation analyses demonstrate the complementary importance of: 1) training on videos versus static images; 2) scaling the magnitude and diversity of the pretraining video corpus; and 3) using diverse objectives that encourage full-stack multimodal reasoning, from the recognition to …
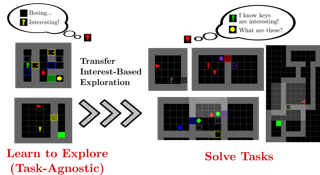
Common approaches for task-agnostic exploration learn tabula-rasa --the agent assumes isolated environments and no prior knowledge or experience. However, in the real world, agents learn in many environments and always come with prior experiences as they explore new ones. Exploration is a lifelong process. In this paper, we propose a paradigm change in the formulation and evaluation of task-agnostic exploration. In this setup, the agent first learns to explore across many environments without any extrinsic goal in a task-agnostic manner.Later on, the agent effectively transfers the learned exploration policy to better explore new environments when solving tasks. In this context, we evaluate several baseline exploration strategies and present a simple yet effective approach to learning task-agnostic exploration policies. Our key idea is that there are two components of exploration: (1) an agent-centric component encouraging exploration of unseen parts of the environment based on an agent’s belief; (2) an environment-centric component encouraging exploration of inherently interesting objects. We show that our formulation is effective and provides the most consistent exploration across several training-testing environment pairs. We also introduce benchmarks and metrics for evaluating task-agnostic exploration strategies. The source code is available at https://github.com/sparisi/cbet/.
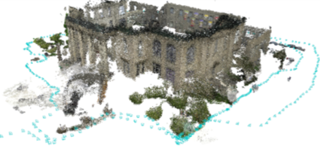
We introduce DROID-SLAM, a new deep learning based SLAM system. DROID-SLAM consists of recurrent iterative updates of camera pose and pixelwise depth through a Dense Bundle Adjustment layer. DROID-SLAM is accurate, achieving large improvements over prior work, and robust, suffering from substantially fewer catastrophic failures. Despite training on monocular video, it can leverage stereo or RGB-D video to achieve improved performance at test time. The URL to our open source code is https://github.com/princeton-vl/DROID-SLAM.
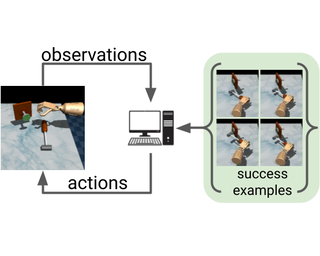
Reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms assume that users specify tasks by manually writing down a reward function. However, this process can be laborious and demands considerable technical expertise. Can we devise RL algorithms that instead enable users to specify tasks simply by providing examples of successful outcomes? In this paper, we derive a control algorithm that maximizes the future probability of these successful outcome examples. Prior work has approached similar problems with a two-stage process, first learning a reward function and then optimizing this reward function using another reinforcement learning algorithm. In contrast, our method directly learns a value function from transitions and successful outcomes, without learning this intermediate reward function. Our method therefore requires fewer hyperparameters to tune and lines of code to debug. We show that our method satisfies a new data-driven Bellman equation, where examples take the place of the typical reward function term. Experiments show that our approach outperforms prior methods that learn explicit reward functions.

Although the fairness community has recognized the importance of data, researchers in the area primarily rely on UCI Adult when it comes to tabular data. Derived from a 1994 US Census survey, this dataset has appeared in hundreds of research papers where it served as the basis for the development and comparison of many algorithmic fairness interventions. We reconstruct a superset of the UCI Adult data from available US Census sources and reveal idiosyncrasies of the UCI Adult dataset that limit its external validity. Our primary contribution is a suite of new datasets derived from US Census surveys that extend the existing data ecosystem for research on fair machine learning. We create prediction tasks relating to income, employment, health, transportation, and housing. The data span multiple years and all states of the United States, allowing researchers to study temporal shift and geographic variation. We highlight a broad initial sweep of new empirical insights relating to trade-offs between fairness criteria, performance of algorithmic interventions, and the role of distribution shift based on our new datasets. Our findings inform ongoing debates, challenge some existing narratives, and point to future research directions.


Cross-modal matching, which aims to establish the correspondence between two different modalities, is fundamental to a variety of tasks such as cross-modal retrieval and vision-and-language understanding. Although a huge number of cross-modal matching methods have been proposed and achieved remarkable progress in recent years, almost all of these methods implicitly assume that the multimodal training data are correctly aligned. In practice, however, such an assumption is extremely expensive even impossible to satisfy. Based on this observation, we reveal and study a latent and challenging direction in cross-modal matching, named noisy correspondence, which could be regarded as a new paradigm of noisy labels. Different from the traditional noisy labels which mainly refer to the errors in category labels, our noisy correspondence refers to the mismatch paired samples. To solve this new problem, we propose a novel method for learning with noisy correspondence, named Noisy Correspondence Rectifier (NCR). In brief, NCR divides the data into clean and noisy partitions based on the memorization effect of neural networks and then rectifies the correspondence via an adaptive prediction model in a co-teaching manner. To verify the effectiveness of our method, we conduct experiments by using the image-text matching as a showcase. Extensive experiments on …
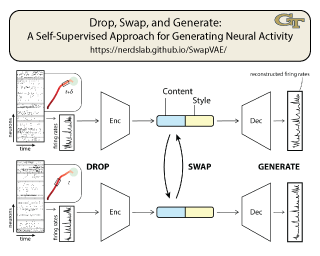
Meaningful and simplified representations of neural activity can yield insights into how and what information is being processed within a neural circuit. However, without labels, finding representations that reveal the link between the brain and behavior can be challenging. Here, we introduce a novel unsupervised approach for learning disentangled representations of neural activity called Swap-VAE. Our approach combines a generative modeling framework with an instance-specific alignment loss that tries to maximize the representational similarity between transformed views of the input (brain state). These transformed (or augmented) views are created by dropping out neurons and jittering samples in time, which intuitively should lead the network to a representation that maintains both temporal consistency and invariance to the specific neurons used to represent the neural state. Through evaluations on both synthetic data and neural recordings from hundreds of neurons in different primate brains, we show that it is possible to build representations that disentangle neural datasets along relevant latent dimensions linked to behavior.
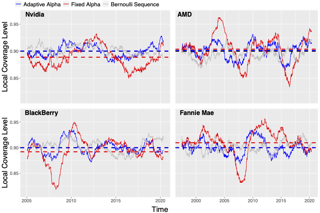
We develop methods for forming prediction sets in an online setting where the data generating distribution is allowed to vary over time in an unknown fashion. Our framework builds on ideas from conformal inference to provide a general wrapper that can be combined with any black box method that produces point predictions of the unseen label or estimated quantiles of its distribution. While previous conformal inference methods rely on the assumption that the data are exchangeable, our adaptive approach provably achieves the desired coverage frequency over long-time intervals irrespective of the true data generating process. We accomplish this by modelling the distribution shift as a learning problem in a single parameter whose optimal value is varying over time and must be continuously re-estimated. We test our method, adaptive conformal inference, on two real world datasets and find that its predictions are robust to visible and significant distribution shifts.

"Monkey see monkey do" is an age-old adage, referring to naive imitation without a deep understanding of a system's underlying mechanics. Indeed, if a demonstrator has access to information unavailable to the imitator (monkey), such as a different set of sensors, then no matter how perfectly the imitator models its perceived environment (See), attempting to directly reproduce the demonstrator's behavior (Do) can lead to poor outcomes. Imitation learning in the presence of a mismatch between demonstrator and imitator has been studied in the literature under the rubric of causal imitation learning (Zhang et. al. 2020), but existing solutions are limited to single-stage decision-making. This paper investigates the problem of causal imitation learning in sequential settings, where the imitator must make multiple decisions per episode. We develop a graphical criterion that is both necessary and sufficient for determining the feasibility of causal imitation, providing conditions when an imitator can match a demonstrator's performance despite differing capabilities. Finally, we provide an efficient algorithm for determining imitability, and corroborate our theory with simulations.